Doran (2021):
Blogger Comments:
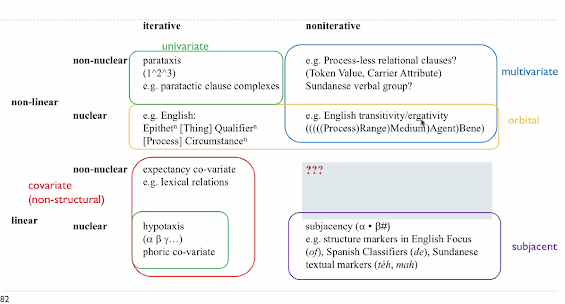
[1] To be clear, the top left cell of the table, [non-nuclear, non-linear], 'parataxis', has not been argued for in this paper. It corresponds to Martin's serial (multi-nuclear) structure, which, as previously demonstrated, is a misconstrual of all logical structure as parataxis.
[2] To be clear, the top right cell of the table, [non-nuclear, linear], 'expectancy covariate', is not a structure type, as later acknowledged by the theorist who first formulated it: Lemke (1989).
[3] To be clear, the bottom left cell of the table, [nuclear, non-linear], 'orbital', only applies to part of a structure, not to the entire structure of a unit. It corresponds to the nucleus-satellite relation in Martin's experiential orbital structure.
[4] To be clear, the bottom right cell of the table, [nuclear, linear], 'hypotaxis', also only applies to part of a structure, not to the entire structure of a unit. It corresponds to the satellite-satellite relation in Martin's experiential orbital structure.
However, there are further inconsistencies in this case. Firstly, in the preceding argument, the example of this category, solar electron neutrons, was categorised as linear, but not nuclear, whereas here it is categorised as both linear and nuclear.
Secondly, the preceding argument for this category was based on experiential structure — relations between Classifiers — whereas here it is reconstrued as a hypotactic logical structure.
Thirdly, the preceding argument for this category was concerned with only part of a structure — relations between Classifiers in a nominal group — whereas here it reconstrued as applying to the structure of the entire unit (nominal group).
[5] In short, Doran has here categorised three of Martin's misunderstandings of structure types — covariate, orbital, serial — in terms of distinctive features. In doing so, he essentially provides a flawed system to specify classes — not functions — in metalanguage — not language — without regard to the metafunctions that the structure types express.